BUN
 |
|
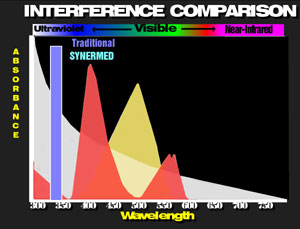 |
BUN Interference Comparison Urea is one of the few serum analytes which can be measured using ultraviolet detection without serious chromatic interference. The reason can be seen from the molar concentration at the upper limit of normal. Urea is one of the most plentiful molecules in serum. Additionally, two molecules of NADH are oxidized per molecule of urea. Thus, the signal [chromophore absorbance] to noise [serum background absorbance] is very favorable, relative to other serum analytes.
-
-
-
-
- Ready-to-Use Liquid Reagent
- Maximal "On Board" Stability
- Eliminates Costly Waste
- No Reagent Preparation
-
-
-
Principles of the Reaction
The Synermed® blood urea (BUN) method is based on the enzymatic conversion of urea to two molecules of ammonia. The ammonia participates in an enzymatic reaction with glutamate dehydrogenase in which NADH is oxidized to NAD. The rate of decrease in absorbance of NADH at 340 nm is proportional to urea concentration.
The reagents are supplied as stable ready-to-use liquids for simplicity of use. The extended "on board" life of the reagents results in economies due to the elimination of wastage and reconstitution time.
urea + H20 -> 2 NH3 + CO2
2 α-ketoglutarate + 2 NH4+ + 2 NADH -> 2 L-glutamate + 2 NAD+ + 2 H20
Analytical Range
Most applications of this procedure have demonstrated linearity to 150 mg/dL (53.5 mmol/L).
Expected Values
The normal range for urea nitrogen in adult human serum is reported to be: 5 to 20 mg/dL (1.8 to 7.1 mmol/L).
Special Performance Characteristics
- The Synermed urea nitrogen methodology was correlated to a widely accepted enzymatic method. The linear regression on 55 samples, run in duplicate, ranging from approximately 6 to 90 mg/dL (2.1 to 32 mmol/L) with Synermed results on the Y-axis gave an equation of Y = 0.98X + 0.7 with a correlation coefficient of 0.999.
- The sensitivity of the procedure is such that an absorbance change of 0.001 will detect as little as 1.3 mg/dL (0.48 mmol/L) urea nitrogen.
- The average within run precision of the method as applied to an automated analyzer was determined by assaying 30 samples of quality control material at two levels of urea nitrogen concentration:
Mean SD CV 15.7 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) 0.36 (0.13) 2.5% 54.5 mg/dL (19.5 mmol/L) 0.56 (0.20) 1.1% - The run to run reproducibility of the method as applied to an automated analyzer was determined from the values obtained by 5 replicate analyses of quality control material assayed over a 23 batch period.
Mean SD CV 15.7 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) 0.48 (0.17) 3.0% 55.5 mg/dL (19.8 mmol/L) 1.30 (0.46) 2.3%
Product Packaging and Storage
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Packaging | Package Volume (mL) | Storage |
| UV190-X | BUN | 1x200 mL + 1x100 mL | 300 | 0-4° C |
| UV190 | BUN | 3x200 mL + 3x100 mL | 900 | 0-4° C |
| UV191-L | BUN Coenzyme | 6x500 mL | 3,000 | 0-4° C |
| UV192-L | BUN Enzyme | 6x500 mL | 3,000 | 0-4° C |
| UV190-911 | BUN | 6x50mL + 3x50mL | 450 | 0-4° C |
| UV190-WK | BUN | 4x25mL + 4x12.5mL | 150 | 0-4° C |
| UV195-X | BUN | 1x200 mL + 1x100 mL | 300 | 0-4° C |
| UV195 | BUN | 3x200 mL + 3x100 mL | 900 | 0-4° C |
| UV193-L | BUN Enzyme | 6x500 mL | 3,000 | 0-4° C |
Connect with us
Certifications
 |
 |
 |
 |
||

